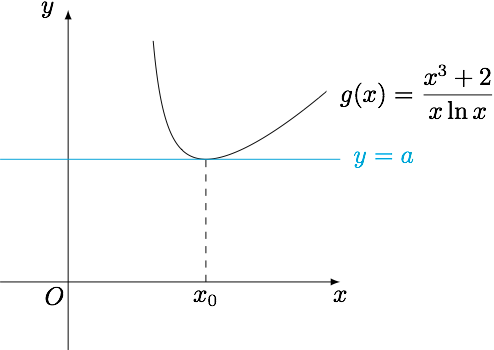若函数$f(x)=x^2+\dfrac 2x-a\ln x$($a>0$)存在唯一零点$x_0$,且$m<x_0<n$,其中$m,n$为相邻的整数,则$m+n=$_______.
分析 根据题意,方程$$x^2+\dfrac 2x-a\ln x=0$$有唯一解,也即函数$g(x)=\dfrac{x^2+\dfrac 2x}{\ln x}$的图象与直线$y=a$相切于$(x_0,a)$.考虑到$a>0$,因此只需要估计函数$g(x)$的导函数在$x>1$时的零点位置即可.
解 函数$g(x)$的导函数$$g'(x)=\dfrac{(2x^3-2)\ln x-(x^3+2)}{x^2\ln^2x},$$设分子为$\varphi(x)$,则$$\varphi(2)=14\ln 2-10<7\sqrt 2-10<0,$$而$$\varphi(3)=52\ln 3-29>0.$$其中用到了$$\ln 2<\sqrt 2-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt 2},$$这是因为对$\ln x$的常用估计:$$\forall x>1,2\cdot\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}<\ln x<\sqrt x-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt x}.$$这样就得到了$$2<x_0<3,$$从而$m+n$的值为$5$.